 |
GDBMS 1.0
|
 |
GDBMS 1.0
|
The main function of the server it creates a GDBMS_USCOREbindingService instance
It runs as a CGI application or a standalone HTTP server
GDBMS
Main characteristics:
Fuly transactional
Supports formalism called labeled directed attributed hypergraph
Users management, sessions, transactions are separated by the transport system, so that different transport system can be used in future
Its own procedural language for definition of triggers and user scripts
Type definition subsystem, which supports class object-like hierarchy structures, arrays definitions, simple types aliases definitions
GDBMS is designed and implemented to support Graph Database formalism called Directed, labeled hyper-graph, which increases the power of the set of applicable tasks which can be solved by such a system. More efficient disk usage is also achieved by using the formalism: 2 or more edges can be represented as 1 hyper-edge. Another important feature of the system is that each of the nodes and edges can be of different user types. User types can be user defined structures, arrays or simple type aliases for integers or strings. The system is transactional, user authentication and authorization, sessions and transactions management. The transactional subsystem is quite sophisticated unlike the transactional subsystems of other lookalike graph database systems. It insures that only those edges or nodes, which have been added or altered by the transaction are in the transactional folder and/or locked by the transaction. Information about the transaction history is maintained, and when transaction close command is received, some edge/node operations dependencies are resolved and handled: Insert after update, update after insert, update after update, for instance. Data is stored in xml based hash table, which balances the relative complexity of search operations and insert and alter operations and achieves easier transactional lock of files when needed. If binary trees were used, much effort on balancing the trees would be required, when insert and update operations occur.The hybrid data model which has relational and hierarchical characteristics is also easily achieved by using multiple hash tables.
Search and iteration operations support limiting the number of results when too big graphs are iterated.
Extreme path queries support relative path user specification to a valid value in a valid type path in the type hierarchy for a node.
The metric in terms to the extreme path queries is a valid type path to a numeric value in each edge, which is used by Dijkstra algorithms to determine which of the paths is longest or shortest. The metric can be determined in a user trigger, specified in a user defined script by a formula or directly, depending on the user application.
The web service interface remote methods, which directly support call of each operations is obsolete and the user is encouraged to use the methods, which allow script interpretation and user script triggers registration and interpretation.
As a conclusion we can claim that the system has everything needed to serve as a basis of a numerous set of applications, which are graph based or hypergraph oriented: routing protocols simulations; map tasks; social networks graphs; Set oriented tasks (Hyperedges can be viewed as a sets of nodes), etc.
The user is able to define its own event handlers. The language is procedural. It supports its own flow identifier operator for graphflow queries for nodes and edges, which is used in combination with foreach operator.
First goto file maininclude.h and change #define MAINFOLDER "main_folder/" to the corresponding folder name of which the service is going to use as its main folder. Then compile the service, by issuing the following command in order to compile the source code:
To use as a standalone iterative, non-multithreaded server, run the command ./[program_name] [port] [some text] To deploy as a cgi application, simply copy the binary file in the cgi folder of your http server The service main function runs according to the following control flow diagram:
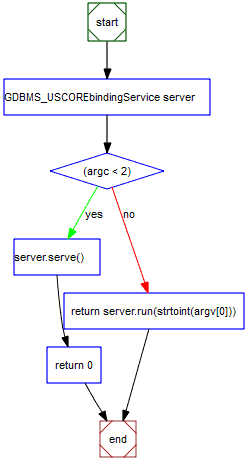
As you can see, it can be either deployed as a cgi application or as a standalone server. If the command line input arguments are less than 2, then it assumes that it is called by a web server and it simply serves as a cgi application. If it is called with at least 2 input command line parameters, it starts its built in standalone non multithreaded http server on tcp port, specified by the 1st input parameter.
In order to operate correctly, the server needs to use disk stored hash tables, by using hash_table class in certain folders hierarchically, as follow. In folder MAINFOLDER/admin/users, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| users | |||
| id | name | pass | gr_id |
gr_id is a foreign key to usergroups relation. The fields id, name, gr_id are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
In folder MAINFOLDER/admin/usergroups, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| usergroups | ||
| id | name | admin |
The fields id, name are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
If admin==1, then the current usergroup is administrative.
In folder MAINFOLDER/admin/sessions, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| sessions | ||
| id | user_id | time_started |
The fields id, user_id are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains currently active sessions. In folder MAINFOLDER/admin/transactions, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| transactions | |||
| id | user_id | graph_id | time_started |
The fields id, user_id, graph_id are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains currently active transactions.
In folder MAINFOLDER/admin/graphs, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| graphs | ||||
| id | name | description | creator_id | t_created |
The fields id, name are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains a set of available graphs in the server.
For each graph, there is a subfolder of admin, which name is the same as the graph id. In such a folder, there are the following subfolders with hash tables inside them:
folder MAINFOLDER/admin/[graph_id]/gr_types, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| gr_types | |||||||
| id | name | parsestr | composite | array | asize | aid | internal |
The fields id, name are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains registered datatypes in the graph.
name contains the name of the type. parsestr contains information if it is a simple type, whether it is int "%d" or floating point number "%f" or a string "%s". Composite equals 0, if it is a simple type, 1 if it is structure and 2 if it is an array of type. array equals 1 if this type is array. If the type is array, asize contains the max size of the array. If the type is an array, aid contains the id of the type of the array elements. If the type is of type structure, then internal contains xml information of the structure members as follow: <tp> <tpi id="1"> <tpi id="2"> ... </tp> where tpi id are the ids of the member types of the structure.
folder MAINFOLDER/admin/[graph_id]/gr_main, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| gr_main | |||
| id | node_maxid | edge_maxid | rights_word |
The fields id, node_maxid are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains general information about the graph. Normally, there is 1 record in it.
node_maxid is the max id of nodes allowed in the graph. it is similar with edge_maxid. Rights_word is an integer that contains information about what different types of users are allowed to do with the graph. One can calculate rights word as follow:
Most significant 4 bits are for user for which graph was created: View bit, Insert Bit, Update Bit, Delete Bit If the corresponding bit is set, the corresponding type of web service operation is allowed for the current graph. The next four bits are for users from the user group of the owner of the graph. And the final four bits are for all other users. The integer is 12 bit, so the no rights word is 0 and the all rights given word is: 4095 or 0xFFF
folder MAINFOLDER/admin/[graph_id]/edges, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| edges | ||||||
| id | name | data | inodes | onodes | type_id | tr_id |
The fields id, name are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains information about the edges in the graph.
Name contains the name of the edge. inodes is a , list of ids of the incoming nodes of the current edge. onodes is a , list of the outgoing nodes ids of the current edge. Data contains XML structured text data, which is stored in the current edge. The names of the XML tags correspond with the names of the corresponding types (the same). If the current type is an array, for example, the tag, containing the value of a[5] is <a[5]> [value] </a[5]>
folder MAINFOLDER/admin/[graph_id]/nodes, a relation (hash table) is used with the following parameters:
| nodes | ||||||
| id | name | data | iedges | oedges | type_id | tr_id |
The fields id, name are indexed, in order the hash_table class to be able to search by those fields.
This relation contains information about the nodes in the graph.
Name contains the name of the edge. inodes is a , list of ids of the incoming nodes of the current edge. onodes is a , list of the outgoing nodes ids of the current edge. Data contains XML structured text data, which is stored in the current edge. The names of the XML tags correspond with the names of the corresponding types (the same). If the current type is an array, for example, the tag, containing the value of a[5] is <a[5]> [value] </a[5]>. type_id is the id of the type of the node.
For the purpose of transactions, there are additional transactional folders:
MAINFOLDER/admin/[graph_id]/[tr_id]/edges
MAINFOLDER/admin/[graph_id]/[tr_id]/nodes
[tr_id] is the id of the active transaction, which user used to add or remove nodes and edges.
The content of those folders is explained in details in tr_twin_ht class doc.

 1.7.4
1.7.4